If you are in 1st year class
And searching for important short questions for your exams preparation than read it out
Here is some short questions from chapter 3 of 1st year
INTRODUCTION
1.Why liquids are less common than solid and gases?
2. Compare the properties of gas, liquid and solids.
3. Define atmospheric pressure, write its various units
BOYLE'S LAWS
4. Define Boyle's law and give its mathematical expression
5. What are isotherms. What happened to their position at higher temperature?
6. The product of pressure and volume at constant temperature is constant quantity. Why?
7. The straight line of graph of P vs 1/V goes closer to pressure axis at higher temperature.why?
CHARLES'S LAW
8. Define Charles's law and give its mathematical expression,
9. Charles's law is not obeyed when temperature is measured on Celsius scale. Justify
10. Write quantitative definition of Charles's law.
11. What is absolute zero. Give its relation with factor 1/273 in Charles's law?
12. Justify that the volume of a gas theoretically becomes zero at -273 °C
13. Define thermometry. What are various scales of thermometry. Convert 80°C to Fahrenheit
GENERAL GAS EQUATION
14. Derive general gas equation
15 Derive the units of R when pressure is in atmosphere and volume in dm3
16. Derive SI units of R
17 Prove that
(Derive an expression for the density of a gas)
18 Derive molecular mass of a gas by general gas equation
AVOGADRO 'S LAW
19. Define Avogadro 's law of gases
20. Justify that I cm3 of H2 and 1 cm3 of CH4 have same no. of molecules although CH4 is 8 times heavy than H2.
DALTONS LAW OF PARTIAL PRESSURE
21. State Dalton's law of partial pressure. Write its mathematical form
22. Derive an expression to find partial pressure of a gas.
23. How will you calculate the partial pressure of dry gas which is collected over water?
24.Why pilots feel uncomfortable breathing at high altitude?
25.why normal air cannot be breathed in deep sea.
26. Explain the application of Dalton's law in the process of respiration
DIFFUSION AND EFFUSION
27 Differentiate b/w diffusion and effusion
28 State Graham's law of diffusion and give its mathematical form
29. Why lighter gases diffuse more rapidly than beavier gases?
KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF GASES
30.List four postulates of KMT of gases
31. State mathematical expression of Kinetic equation and root mean square velocity?
32. Explain Boyle's law, Charles's law, Graham's law and Avogadro's law in light of KMT.
LIQUIFICATION OF GASES
33. Define critical temperature, pressure and volume of a gas.
34. Define joule Thomson effect. Why it is not applicable to H, and He. (NH3 can be liquified casily but H2 does not. Why)?
35. What is cause of Joule Thomson effect?
36. Explain linds 's method of liquification of gases.
NON-IDEAL BEHAVIOUR OF GASES
37. Why gases deviate from ideal behavior at high pressure and low temperature?
38.At which conditions gases deviate from ideal behavior?
39.What is compressibility factor. Write its value for ideal gas,
40.H2 and He are ideal at room temperature but SO2 and Cl2 are non-ideal. Why?
VANDER WALLS EQUATION FOR REAL GASES
41. Why pressure correction is done by Vander Wall?
42.What is excluded volume?
43.Give physical significance of Vander wall 's constant a & b
44.Describe SI units of a & b
PLASMA STATE
45. What is plasma. How it is formed?
46. Classify plasma as natural and artificial
47 Write two characteristics of plasma.
48 Where is plasma found?
49. Write four applications of plasma


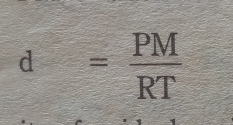

Comments
Post a Comment